The booming IV hydration spa industry operates with virtually no oversight or data backing up its claims, according to the first comprehensive analysis of the spa clinics.
Source link
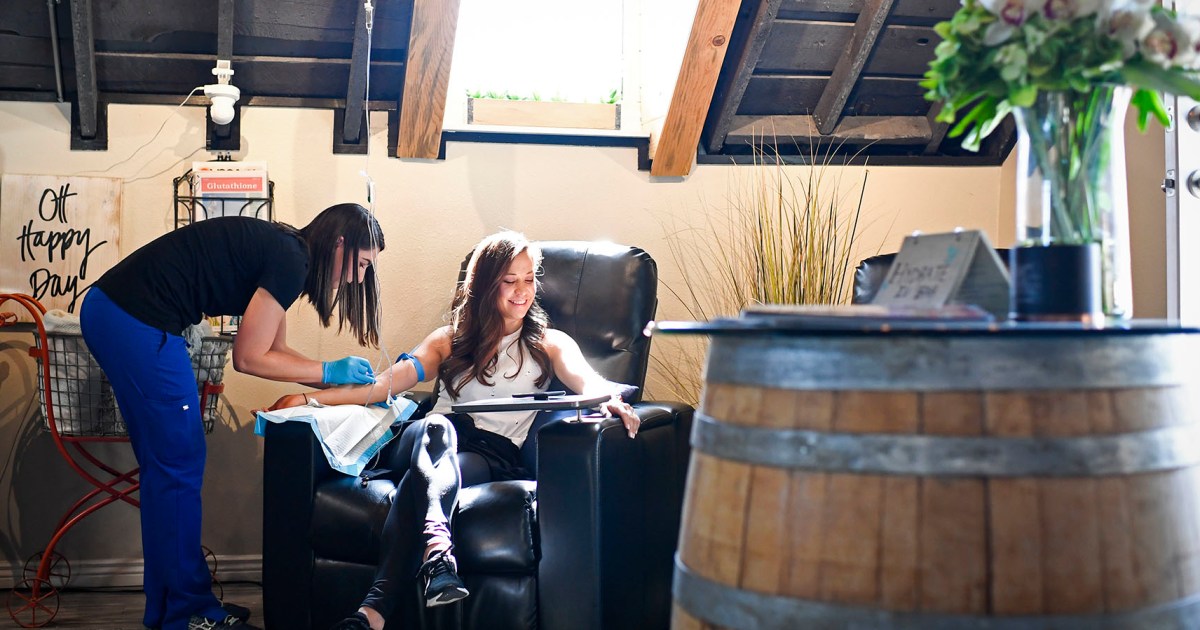
Savewith a NBCUniversal ProfileCreate your free profile or log in to save this articleOct. 6, 2025, 6:07 PM EDTBy Erika EdwardsThe booming IV hydration spa industry operates with virtually no oversight or data backing up its claims, according to the first comprehensive national analysis of hydration clinics. At clinics nationwide, people pay hundreds of dollars to have vitamins and minerals dripped directly into their veins as a detox, to ease headaches or boost immunity, “almost completely without evidence,” said Dr. Peter Lurie, president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest and co-author of the study, published Monday in JAMA Internal Medicine. “As a result, there’s a real danger to consumers.”Hydration clinics, combined with the growing number of med spas offering intravenous vitamin drips, skin care and cosmetic procedures, have ballooned into a $15 billion wellness industry in recent years, according to the American Med Spa Association. The group represents med spas, which often offer IV treatments, nationwide. Alex Thiersch, chief executive officer of the American Med Spa Association, said some IV hydration clinic providers don’t realize that they’re actually practicing medicine and may lack proper training.“We have had folks who are surprised by that,” Thiersch said. “They thought, ‘I’m just doing an IV. It’s different. It’s vitamins.’”“If you’re putting a needle in someone’s vein,” he said, “that’s 100% medical practice.”There are no federal health regulations or national standards for procedures for med spas. Instead, the facilities fall under the authority of each state.As of June 2024, no state or jurisdiction had enacted legislation specifically to regulate IV hydration spas, according to the new study.Thirty-two states did have some kind of policy addressing IV hydration spas, including rules either for prescribing or compounding drugs or how clinics should dispense medications.Four states — Alabama, North Carolina, South Carolina and Vermont — had the most comprehensive oversight. “This is a medical system that exists largely outside of conventional medicine,” Lurie said. “We’re worried that people will spend their money on these without reason to expect benefits. We’re also worried that there will be adverse effects related to this.”The potential for injury is real: Products or equipment could be contaminated, or a provider might not have appropriate training to give an IV safely.There’s no official count of the number of people injured at med spas. Infections and allergic reactions aren’t often reported to health departments. The new research cited NBC News’ previous reporting on med spas as evidence of “rising concerns of their safety, with reports of infections and contaminated products.” Of 255 clinic websites analyzed, more than half offered IV hydration therapy touting therapies like magnesium for headaches and muscle cramps, glutathione as a potential immune system booster, or other substances advertised to increase energy.Just two of those sites listed tangible sources for those health claims. None mentioned potential risks, like infection or allergic reactions. One aspect of the research involved a secret shopper investigation, in which researchers placed calls to 87 randomly chosen spas.Only about 1 in 4 required a medical consultation beforehand. More than 85% recommended specific IV cocktails when callers mentioned symptoms like a headache or cold, often without verifying a patient’s medical history.Fewer than 1 in 4 warned about potential side effects, like bruising or infections. The Food and Drug Administration previously warned consumers about the potential for severe infections and skin deformities from unauthorized shots touted to dissolve fat at med spas.Erika EdwardsErika Edwards is a health and medical news writer and reporter for NBC News and “TODAY.”