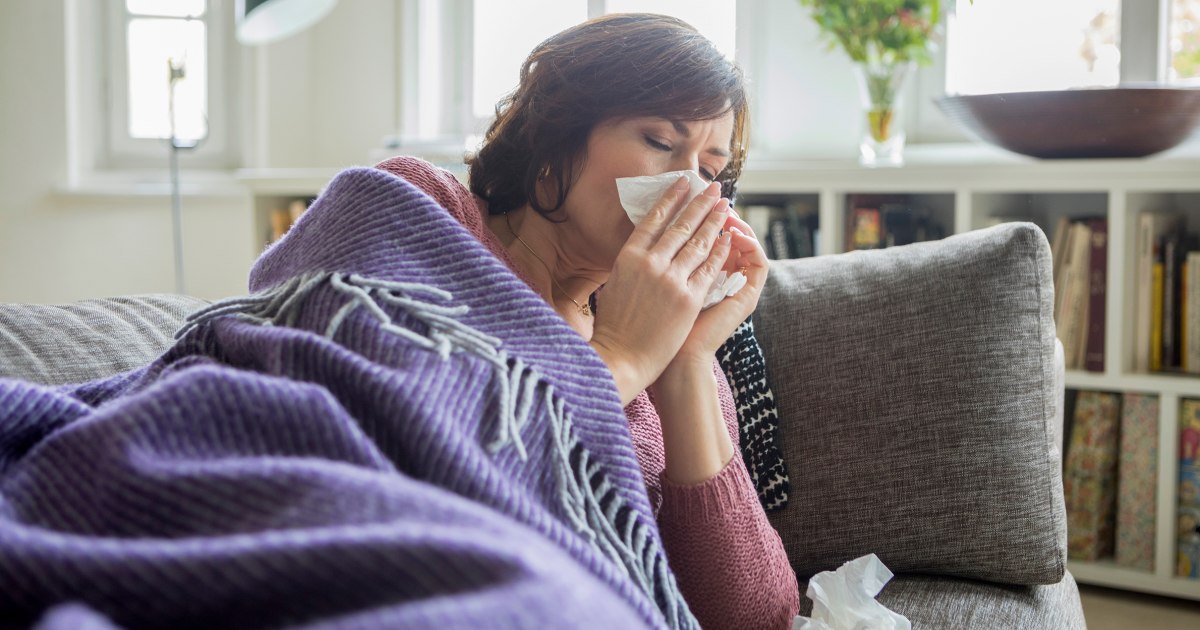
After a rough, record-setting flu season, doctors and health officials are bracing for another wave of fever, misery and respiratory distress.
Source link
Oct. 18, 2025, 7:00 AM EDTBy Mustafa FattahAfter a rough, record-setting flu season, doctors and health officials are bracing for another wave of fever, misery and respiratory distress. In the U.K., health officials are warning about an early rise in flu levels among children and young adults. In Japan, health officials recently declared a flu epidemic and closed schools after experiencing an unusually high number of flu cases early in the season. What does that mean for the U.S.? Typically, flu cases start to rise in November, along with RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) and enteroviruses, and peak in February. But job-cut chaos at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the government shutdown could make it hard to know how the virus is playing out this fall, experts worry. The CDC’s last influenza report for the U.S. was for the week ending Sept. 20, when there was minimal activity. Angela Rasmussen, a virologist at the University of Saskatchewan, is concerned about the possibility of limited flu surveillance by the CDC, leaving the U.S. blind to the scale and scope of flu outbreaks.“Everything from outreach campaigns to more logistical efforts to actually get vaccines out” could be affected, Rasmussen said. “That information just may not be available, so it will be very difficult to coordinate a national response,” she said.Last year’s flu was harsh. There were about 1.1 million hospitalizations associated with the flu, the highest rate in 14 years, according to the CDC. And there were the highest number of doctor visits for flu-like illnesses in more than a decade. An estimated 38,000 to 99,000 deaths were associated with the 2024-2025 flu season, according to a preliminary assessment by the CDC. For kids, it was one of the deadliest years on record: 280 children died from flu. At least three of those children died this June and July, far outside of the typical flu season.How bad will the flu be? Flu is notoriously hard to predict, and this year, things are already looking a little different. The CDC predicted at the end of August that this flu season will be more moderate than last year’s. However, there’s the possibility that some age groups could be hit hard, especially if people don’t get their flu shots. The main strains of flu currently circulating are similar to those that caused the severe outbreaks last season: H1N1 and H3N2 for flu A, as well as flu B. “It’s a little early to know which strains will predominate this year for flu season, but certainly there is risk that similar very virulent strains could circulate again this year,” said Dr. George Diaz, a fellow of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and chief of medicine at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Washington. “This prediction for a moderate season could be off, and it could be another severe flu season,” he said.“We’re still very early in the flu season in North America, and it’s a little hard to know with certainty,” he added. Even if someone got the flu last year, they’ll still be vulnerable to the new version because immunity wanes over time, especially in older people and the immunocompromised, experts say. When is the best time to get the flu shot? The strain is only one factor in how bad it could be this year. Vaccine hesitancy and a weakened public health infrastructure in the U.S. could contribute to flu spread. “It’s going to be largely driven more by social and policy changes than it is going to be driven by virologically related ones,” Rasmussen said.Last flu season, less than half of kids were vaccinated against the flu, a decline of over 20 percentage points from the 2019-2020 season. This year, that trend is expected to continue, said Rasmussen.Dr. William Schaffner, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, said that it’s difficult to know how severe it will be this year in the U.S, but that it’s very unusual to have “two ultra-severe seasons back to back.” So, even though the virus hasn’t changed much, getting vaccinated is the best way to protect against the worst of the season.“October is the ideal time to get vaccinated,” he said. “That ought to provide quite reasonable protection throughout what we consider the influenza season, through February and into March.”Mustafa FattahMustafa Fattah is a medical fellow with the NBC News Health and Medical Unit.